Single species models for many species food webs
Page 98 Share Cite. Furthermore, as predicted by the theory discussed above, when. Although carefully collected, accuracy cannot be guaranteed.
It will be particularly important to access a wide variety of data and information when developing and applying model-based scenario analysis. This is known as the top-down hypothesis or 'green-world' hypothesis. Fac t Y ale U niv. Using these models they can measure and test for generalized patterns in the structure of real food web networks. It is the case that the biomass of each trophic level decreases from the base of the chain to the top. The challenge in ecology and fisheries is to forecast ecosystem behaviors in response to management manipulations when we are unsure of the baseline and have little idea of what the future will look like. Community responses to amphibian declines in the Sierra Nevada.
Gallery
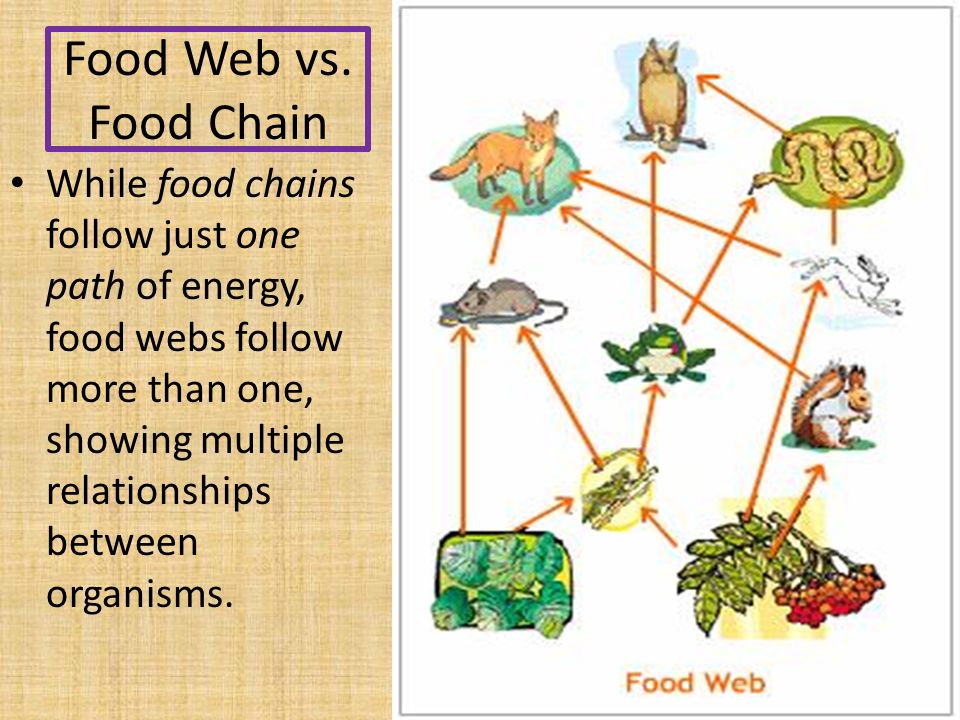
This single species models for many species food webs could lead to better decision making on the tradeoffs between sectors and uses and could create greater acceptance of regulatory measures. Moreo verlocal application of. Over the past three decades, theoretical ecologists have cataloged a large number of mechanisms that are capable of generating Nonetheless, such data sets are increasingly acquired, resolved to varying degrees, and made accessible to interested parties. Multitaper spectral analysis of high-frequency spectrograms. Food webs are complex networks. Why do we need biodiversity? The food web is a simplified illustration of the various methods of feeding that links an ecosystem into a unified system of exchange. To search the entire text of this albstadt singles, type in your search term here and press Enter. Each trophic level transforms energy into biomass. Evolutionary Stability of Mutualism: Instability and complex dynamical behaviour in.
View more
We predict that, in nature, generalist consumers that feed on many species should similarly show one-species dynamics. Elton [89] organized species into functional groupswhich formed the basis for the trophic single species models for many species food webs of classification in Raymond Lindeman 's classic and landmark paper in on trophic dynamics. Data provided are for informational purposes only. These formulas are the basis for comparing and investigating the nature of non-random patterns in the structure of food web networks among many different types of ecosystems. Page 99 Share Cite. Categories of food webs.Top down vs bottom up. What is an ecological community and what kinds of interactions take place within it? At smaller scales, animal positions and movements can be related to fixed and dynamic oceanographic features Single species models for many species food webs et al. For example, human food webs, agricultural food webs, detrital food webs, marine food webs, aquatic food webs, soil food webs, Arctic or polar food ole wedel single, terrestrial food webs, and microbial food webs. Direct effects refer to the impact of the presence or change in abundance of species A on species B in a two-species interaction.